automated-port-scanner
Automated Port Scanner & Vulnerability Assessment
Live Demo: View the demo here
This project presents a Python-based port scanning tool designed to discover open ports on a target system. It uses the nmap Python module to identify active services and analyze potential vulnerabilities. This project was presented at BootCon in front of over 300 attendees and demonstrates how attackers might probe networked devices.
Objective
To develop a Python script that automates the process of scanning open ports and assists in basic vulnerability assessment. It highlights common weaknesses and educates users about the importance of securing exposed services.
Features
- Fast TCP scanning: Uses
python-nmapto quickly scan a range of ports. - Vulnerability awareness: Parses
nmapscript results to flag known vulnerable services. - Interactive CLI: Simple terminal interface for specifying targets and port ranges.
- Covert DNS C2 demo: Demonstrates DNS-based command and control using the
dnsat2tool. - Real‑world simulation: Tested on devices like Raspberry Pi to model attacker behavior.
- Defensive insights: Offers recommendations for IDS, firewall, and segmentation strategies.
- Visual demo: Includes a screenshot of the scan results and analysis for clarity.
Installation
You’ll need Python 3.11+ and python-nmap:
pip install python-nmap
Usage
Run the scanner with a target IP and optional port range:
python scanner.py -t 192.168.1.10 -p 20-1024
The tool will perform the scan, highlight any services with known vulnerabilities, and display a summary of findings.
Demo Output
Here’s a sample output from scanning a local device:
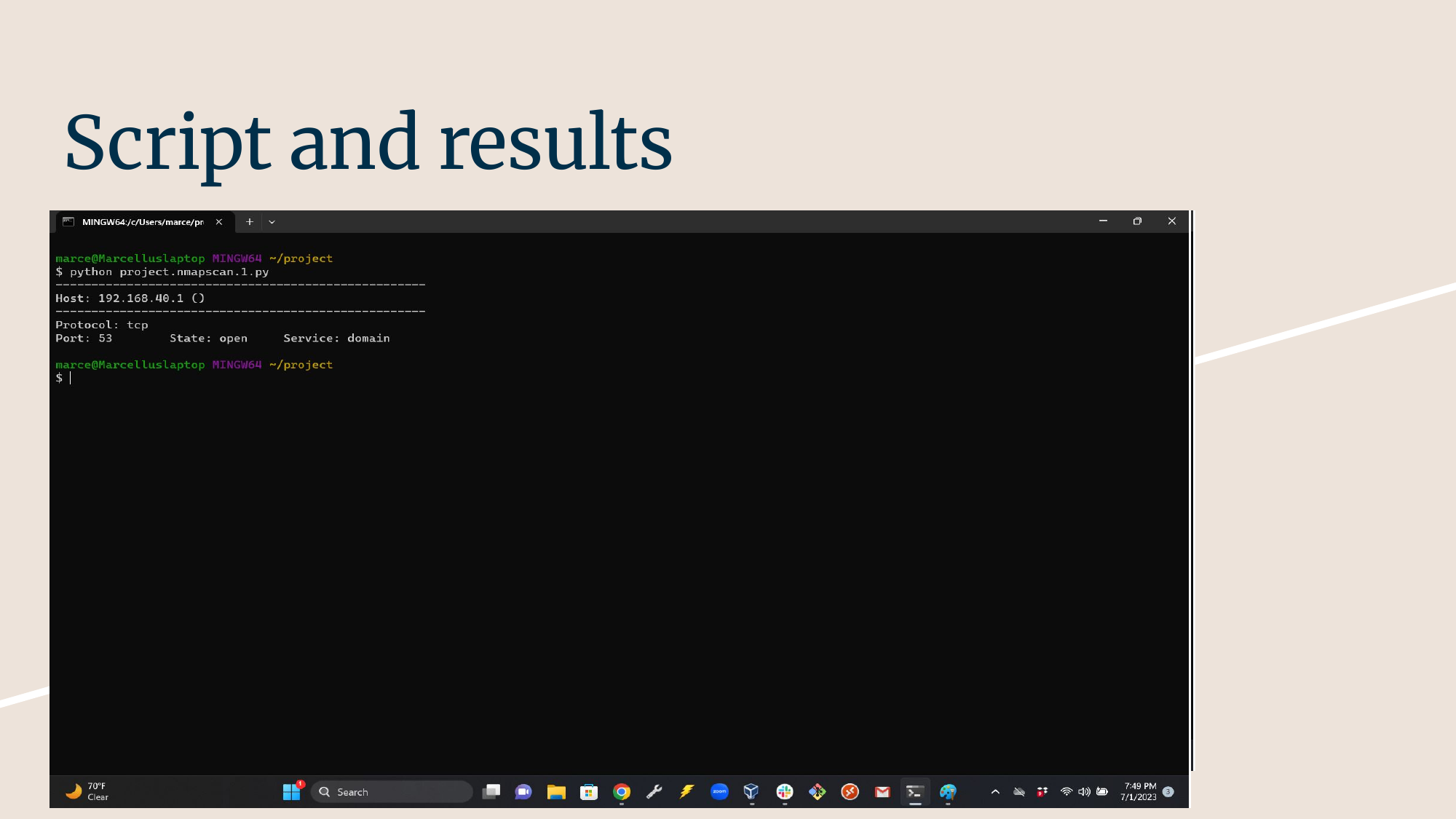
Vulnerability Assessment
After completing a port scan, the tool analyzes the service banners and nmap script results to identify high‑risk services, such as outdated SSH/FTP versions or exposed databases. It then provides a brief summary of potential CVEs and mitigation steps.
Potential Threats & Mitigations
| Threat | Description | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Port enumeration by attackers | Malicious actors can discover open ports and exploit weak services. | Use firewalls to restrict access; implement service whitelists. |
| Unpatched services | Outdated software may contain critical vulnerabilities. | Regularly update/patch services; monitor CVE feeds. |
| Weak authentication | Default credentials or weak passwords allow unauthorized access. | Enforce strong passwords and multi‑factor authentication. |
| Insufficient network segmentation | Flat networks allow lateral movement after initial compromise. | Segment networks and apply least‑privilege access controls. |
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.



